Photo Gallery
 |
Intezer Analyze™

Additional Info
| Company | Intezer |
| Company size | 10 - 49 employees |
| Website | https://www.intezer.com/ |
NOMINATION HIGHLIGHTS
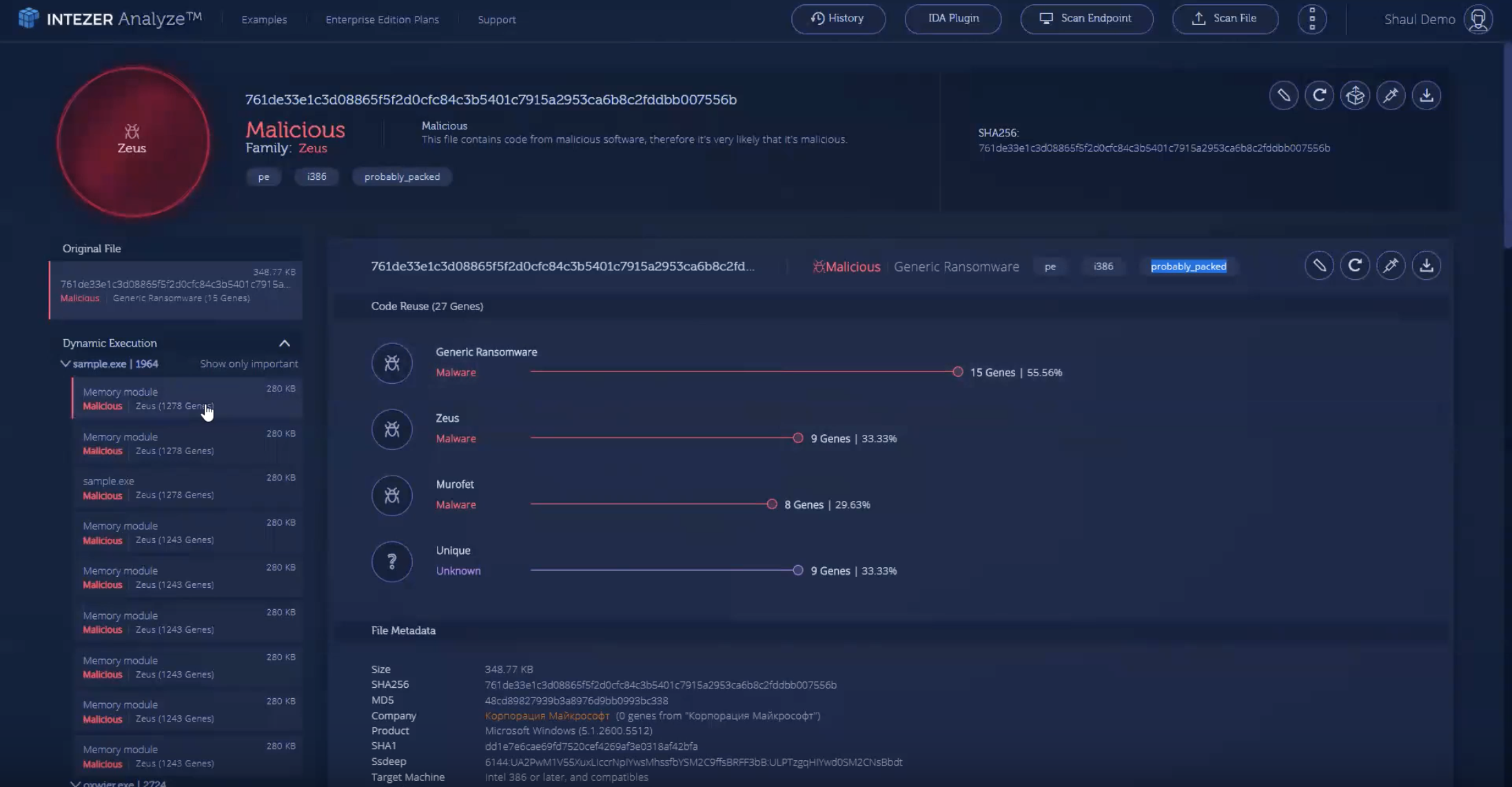
Intezer Analyze™ provides automated and rapid malware analysis, helping users improve their security operations, enrich threat intelligence, and accelerate incident response
By identifying code reuse and similarities between software, users effectively reduce false positives, detect and classify malware, and prioritize alerts according to risk and severity
Users can also leverage Intezer Analyze’s endpoint analysis feature to detect advanced in-memory threats, such as malicious code injections, packed, and fileless malware
Watch this short (1-minute 40 second) demo on our YouTube channel. Demo’d features include hash lookup, dynamic unpacking of a malicious payload, code and string reuse, related samples and additional context about the Zeus malware, which are all features available to community users: https://youtu.be/vGHPQQ7zVoo
How we are different
• Regardless of platform or architecture, binary code reuse is prevalent in every malware family. As long as you have the threat's code indexed, you will be able to detect any variant or new threat which uses even tiny portions of the same code
• The majority of security solutions do not classify malware. Intezer Analyze classifies malware and in many cases can attribute the threat actor behind the attack. This info is helpful for prioritizing and properly responding to incidents. After all, the type of threat (adware vs. banking trojan vs. a nation-state threat, for example) will help to determine the appropriate response path
• In 2019, the number of users leveraging the free Intezer Analyze community edition (analyze.intezer.com) doubled from beginning to year end. The most common threat detected by the community was Emotet. Despite efforts by Emotet to evade detection, Genetic Malware Analysis is effectively able to detect this type of threat by identifying code similarities, regardless of variants that form as new evasion techniques are used

Vote by Sharing
- Like
- Digg
- Tumblr
- VKontakte
- Buffer
- Love This
- Odnoklassniki
- Meneame
- Blogger
- Amazon
- Yahoo Mail
- Gmail
- AOL
- Newsvine
- HackerNews
- Evernote
- MySpace
- Mail.ru
- Viadeo
- Line
- Comments
- SMS
- Viber
- Telegram
- Subscribe
- Facebook Messenger
- Kakao
- LiveJournal
- Yammer
- Edgar
- Fintel
- Mix
- Instapaper
- Copy Link
Each completed social share counts as a vote for this award nomination.



